Encryption SSL Certificates for Secure Data
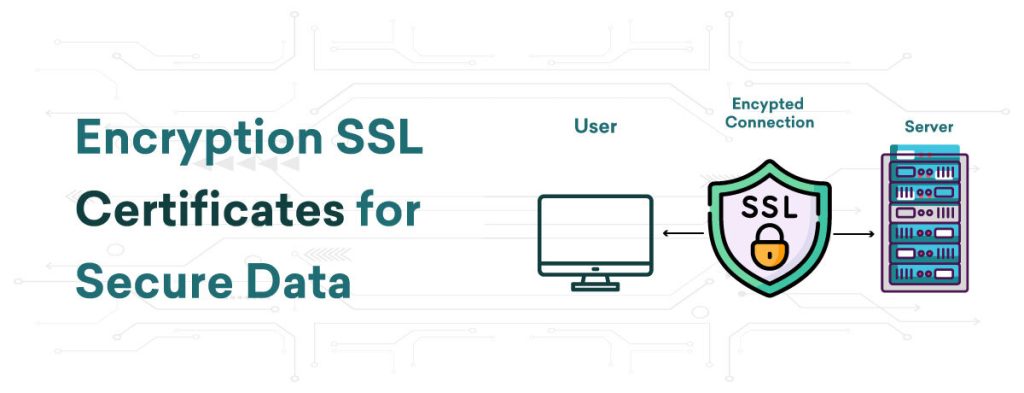
Data and communication security is critical in all areas of cloud computing. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates are among the most important instruments for guaranteeing this security. To prevent data from being intercepted or altered, SSL Certificates encrypt data being passed between a server and a client. Encryption plays a vital role in protecting the confidentiality and accuracy of data, particularly in virtual spaces. Let’s examine SSL certificates, their significance, and how cloud computing might improve encryption and management.
SSL Certificates
SSL Certificates are digital certificate that provides a secure, encrypted connection between a web server and a client (such as a web browser). When a website has an SSL certificate, it means that the data transmitted between the user’s browser and the website is encrypted, making it difficult for hackers or unauthorized parties to read or alter the information.
Why Is SSL Encryption Important?
Data Protection: SSL encryption ensures that sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card numbers, and personal data, is protected from eavesdroppers. Without encryption, this data could be intercepted and used maliciously.
Trust and Credibility: Websites with SSL certificates display a padlock icon in the browser address bar, signaling to users that their connection is secure. This builds trust with visitors and reassures them that their data is safe.
SEO Benefits: Search engines like Google prioritize secure websites in their rankings. Having an SSL certificate can improve your website’s visibility and search engine ranking, driving more traffic to your site.
Compliance: Many industries have regulations requiring data encryption to protect customer information. SSL certificates help businesses comply with these regulations, avoiding potential legal issues and penalties.
How Does SSL Encryption Work?
SSL encryption involves several steps to secure data transmission:
Handshake Process: When a user connects to a website, the server and the client perform an SSL handshake. During this process, they agree on the encryption method and exchange keys.
Certificate Validation: The server presents its SSL certificate to the client. The client verifies the certificate’s authenticity through a certificate authority (CA). If the certificate is valid, the connection proceeds; otherwise, the client will be warned.
Encryption and Decryption: Once the handshake is complete, data is encrypted using a symmetric key. This means that the data is scrambled into an unreadable format. Only the intended recipient, who has the decryption key, can unscramble and read the data.
Secure Communication: Throughout the session, data remains encrypted, ensuring that any information exchanged between the server and client is protected.
Managing SSL Certificates in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing platforms provide various tools and services to manage and encrypt SSL certificates efficiently. Here’s how cloud solutions enhance SSL certificate management:
Automated SSL Provisioning: Many cloud services offer automated SSL certificate provisioning. This means that you can obtain and install SSL certificates with minimal manual intervention. Automated processes reduce the risk of errors and ensure timely updates.
Centralized Management: Cloud platforms often provide centralized management tools for SSL certificates. This allows businesses to monitor and manage their certificates from a single dashboard, simplifying the administration process.
Scalability: Cloud environments can easily scale to accommodate increased traffic and additional domains. With cloud-based SSL solutions, you can manage SSL certificates for multiple subdomains and domains without worrying about hardware limitations.
Renewal Reminders: SSL certificates have expiration dates, and failing to renew them can lead to security warnings and service disruptions. Cloud services often include renewal reminders and automatic renewal options to ensure that certificates are always up-to-date.
Integration with Other Services: Cloud providers often integrate SSL certificate management with other security services, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems. This creates a comprehensive security framework, enhancing overall protection.
Steps to Encrypt SSL Certificates in the Cloud
Choose a Cloud Provider: Select a cloud provider that offers SSL certificate management services. Popular options include AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
Obtain an SSL Certificate: Purchase or obtain an SSL certificate from a trusted certificate authority. Some cloud providers offer free SSL certificates as part of their services.
Install the Certificate: Use the cloud provider’s tools to install the SSL certificate on your cloud-based server. Follow the provider’s instructions for proper installation.
Configure Security Settings: Configure security settings to ensure that SSL encryption is enabled for all relevant services and applications. This includes setting up secure protocols and cipher suites.
Monitor and Renew: Regularly monitor the status of your SSL certificates and set up renewal reminders. Ensure that certificates are renewed before they expire to maintain continuous protection.
Conclusion
SSL certificates are a critical component of online security, ensuring that data transmitted between servers and clients is encrypted and protected. In the world of cloud computing, managing and encrypting SSL certificates becomes easier with automated tools, centralized management, and seamless integration with other security services. By leveraging cloud-based SSL solutions, businesses can enhance their security, build trust with users, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. With robust SSL encryption, companies can confidently protect their data and maintain a secure online presence.
Good https://is.gd/tpjNyL
Very good https://lc.cx/xjXBQT